What is Melanin?
Have you ever wondered where there are people with varying skin color? Some have dark skin, others are brown, while many people are pale or almost white. The difference in skin color in people is due to the presence and absence of melanin. So, “What is Melanin?”
Melanin is the pigmentation responsible for the color of the skin, hair, and stria vascularis of the inner ear and eye. It is also found in the zona reticularis of the adrenal gland and brain tissues such as the medulla and locus coeruleus. Melanin is produced by melanocytes and found in every living person, except the number of melanocytes differs from person to person.
The more melanocytes present, the more pigmented a person becomes and the increase in melanin metabolism. This natural body pigment is concentrated in different parts of the body and can cause intense pigmentation in the concentrated areas, causing hyperpigmentation.

What Does Melanin Deposits Do To Your Face?
Excess melanin deposits on your face can cause a common skin condition called Hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation is a skin condition that makes certain parts of your face darker than others, causing brown, black, gray, or even red patches on your face.
It is common with People of Color (PoC), especially dark or brown people with higher melanin content. Dark spots or hyperpigmentation can be triggered by burns, rashes, acne, or other trauma to the skin. There are different kinds of hyperpigmentation and they include:
- Age Spots or Liver Spots: As people begin to age, particularly those with fair skin who spend a lot of time under the sun, dark spots can begin to appear on sun-exposed areas such as their face, arms, hands, and shoulders.
- Melasma: This hyperpigmentation is a result of hormonal imbalance. It often affects pregnant women and women suffering from PCOS.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: It is a common kind of hyperpigmentation that occurs after trauma to the skin. When your skin experiences inflammatory conditions like acne, it can trigger excess melanin production during and after treatment.
What Causes Melanin to Increase?
Melanin production is necessary to maintain the skin's pigmentation, however, exposure to certain conditions can trigger excessive melanin in the skin.
- Sun exposure: There are many melanin triggers in the body and a common trigger is the Sun. Constant sun exposure can cause the body to produce more melanin than usual, which is a protective response against UV rays. When the body is exposed to UV radiation, it produces free radicals due to oxidative stress. The free radicals alongside the UV radiation trigger melanocytes which cause melanin pigments (red or black) in the body.
- Excessive Vitamin Intake: Certain vitamins increase melanin production in the body. Vitamin A, a powerful antioxidant found in green leafy vegetables has been linked to melanin production.
- Tanning: Using tan beds can also increase melanin production on your skin as it operates in the same manner as being exposed to sunlight.
- Trauma to the skin: Trauma or inflammatory triggers like burns, acne, and eczema can increase melanin during healing.

What Happens When Melanin Is Low?
Excessive melanin production is often the interest of many, but rarely do people talk about low melanin production. Low melanin production can result in several skin conditions and a common one is Albinism.
Albinism is a genetic skin condition that is inherited due to the presence of autosomal recessive genes in both parents. That is both parents carry a mutated gene that is passed down to their young one. There are numerous types of albinism, but the most common is oculocutaneous albinism type 2. It is prevalent among people of African descent and appears as a reduction or complete absence of melanin on the skin, eyes, and hair. Usually, the statistics of oculocutaneous albinism type 2 in African Americans is around 1 in 10,000, in Africans is around 1 in 2000, and in white Americans it is 1 in 36,000.
Another result of melanin deficiency is deafness in people with Waardenburg's syndrome. Although most people with Waardenburg's syndrome have normal gearing, deafness is common among the Hopi people in North America.
Melanin vs Melatonin: What's the Difference?
In human biology, the terms melanin vs melatonin are often used to mean the same thing phonetically, while they are different words that play unique roles in the body.
Melanin, as mentioned earlier, is a natural pigment produced by melanocytes and is responsible for the color of the skin, hair eyes, and ears. It protects the skin against harmful UV radiation and can exist as black or brown (Eumelanin) and yellow or red (pheomelanin)
Melatonin is a hormone synthesized by the pineal gland in the body in response to a darker environment. It is responsible for the circadian rhythm and consoles the body's sleep-wake clock. It is produced more at night to allow you to sleep properly and keep you awake during the day as it is sensitive to light. Melatonin supplements are readily sold in the supermarket and are often recommended for people with poor sleeping patterns.
Overall, melanin and melatonin are two compounds that function differently in the body.
How To Reduce Melanin in Skin?
With the rise in hyperpigmentation, people are in search of how to reduce melanin production on their skin and to ensure a uniform skin color. There are many ways to reduce melanin in your skin and they include:
- Consistent Use Of Sunscreens: Sunscreens are skin products that protect your skin against UV radiations that trigger melanocytes to produce melanin. When you plan to go into the sun, ensure you rub sunscreen with an SPF of 30 and above to block harmful rays. Sunscreens do not provide 24-hour protection against the sun, so you need to reapply every 4 hours or as stated by the product.
- Limit Your Exposure To The Sun: A guaranteed way to avoid UV rays is to avoid going into the sun. Limit your exposure to the sun and stay indoors. You can avoid going out when the sun's intensity is at its highest, particularly between 10 am to 3 pm.
- Wear Protective Clothing: If you plan on going out into the sun, wear protective clothing such as sunglasses, long-sleeved dresses, long flower dresses, and full-coverage hats to protect your skin from the sun and promote melanin reduction.
- Avoid Tanning: Limit the use of tanning beds and creams if you want to get rid of melanin in your skin.
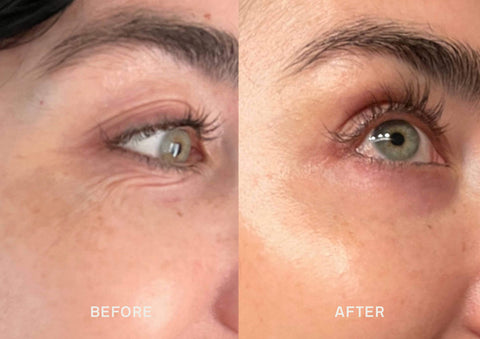
How To Prevent Melanin Production?
While you cannot prevent the total production of melanin, especially if you are dark or brown, you can control its production. If you are looking for solutions on how to lower melanin or how to reduce melanin production, the following skin treatments can help:
- Laser Therapy: With laser therapy, you can reduce or even prevent melanin production. Laser therapy uses a pulse light technology on your skin's surface to reduce melanin deposits. Ablative Laser Technology is a common laser therapy designed to treat skin discoloration by removing the outer layer of the skin, containing melanin deposits to reveal the lighter skin layer. It can remove melanin facial deposits or melanin in any other parts of the body.
- Kojic Acid: Kojic acid is a skin-lightening compound that creates a barrier between your skin and the formation of tyrosine which is responsible for melanin production. This skin component is a melanin inhibitor that prevents further melanin production and makes the skin lighter.


Leave a comment